WHAT IS BANKING SYSTEM? BANKING IN INDIA
This can be defined as a structural network of institutions that offer financial services within a county in other to promote the financial stability growth of that county. The typical performance of the institution includes: commercial banks that take deposits and make loans, investment banks that specialize in capital market issues and trading, and national central banks that issue currency and set monetary policy.
When we talk about the banking industry we only look at certain things such as withdrawal of money, saving, granting of loan and insurance e.t.c. but is more than that because it plays a major role in maintaining the economic stature of a country. Given their importance in the economy, banks are kept under strict regulation in most of the countries. We will be looking into India banking the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the apex banking institution that regulates the monetary policy in the country and also promotes stability in the financial status of the country.
India’s banking sector has been growing so fastly and versatile and have the financial power in the world, India banking is divided into a major different part which is Rural and Urban. Each group has its benefits and limitations in their operations. They have a dedicated target market. Some are concentrated on their work in the rural sector while others in both rural as well as urban. Most of them are only catering in cities and major towns in promoting economic growth not only by channeling savings into investments but also by improving the allocative efficiency of resources than by channeling of resources from savers to investors.
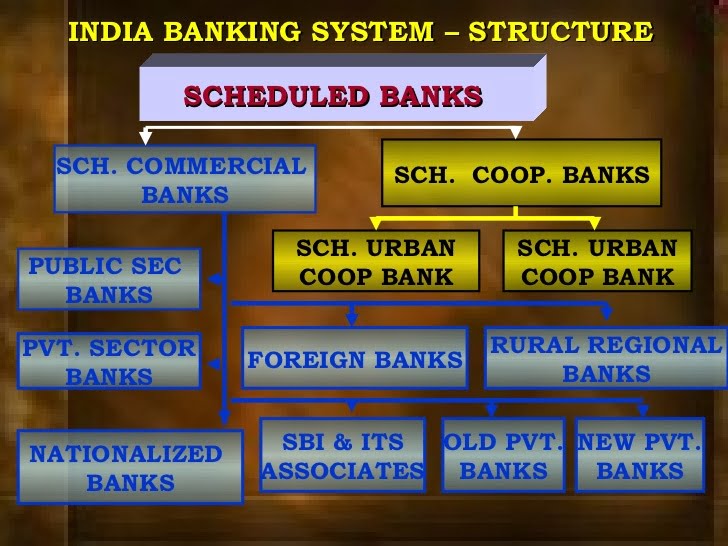
Banking institution especially banking system of India consists of the central bank (Reserve Bank of India – RBI), which is divided into commercial banks, cooperative banks, and development banks (development finance institutions). These institutions, which provide a meeting ground for the savers and the investors, form the core of India’s financial sector.
let check out the classification of banks in India we will say we have different categories of bank categories which are
1. Commercial Banks
Along with the rest of the economy and perhaps even more than the rest, financial markets in India have witnessed a fundamental transformation in the years since liberalization through Commercial Banking. Commercial Banks are regulated under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 and their business model is designed to make a profit but their major motive is to accept deposits and grant loans to the general public, corporate and government. India Commercial banks have grown wide with their services to an extent they have to carve out some branch which are
- Foreign banks
- Public sector banks
- Regional rural banks( PRB)
- public sector Banks
The going has not been smooth all along but the overall effects have been largely positive base on the branch that was curved out to allocate their services for the benefit of the citizen.
2. Co-operative Banks
Cooperative banks are classified into urban and rural which are well known. Apart from these, a fairly new addition to the structure is payments bank. Co-operative banks are registered under the Cooperative Societies Act, 1912 and they are run by an elected managing committee. The benefit of cooperative is to make sure to maintain the stability of finance in the sense that they make no-profit and no-loss basis and mainly serve entrepreneurs, small businesses, industries and self-employment in urban areas. In rural areas, they mainly finance agriculture-based activities like farming, livestock, and hatcheries.

3. Payments Banks
Payment banks is a new model of the banking industry which is conceived by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Both the current accounts and savings accounts can be operated by such banks. Payments banks can issue services like ATM cards, debit cards, net-banking, and mobile-banking.
4. Small Finance Banks