2022 Waec Biology practical specimen Answer has been solved here. If you are a candidate who is in search of a 2022 Waec biology practical specimen answer then you are at the right website because we have answered the 2022 Waec biology specimen questions which were provided, to make sure all our audience passes with the solution if they study it carefully.
Nkedugists don’t charge any fee for providing help or services to our audience, the only thing is to bookmark or subscribe to our website for you to have the latest updates.
If you are asking if the 2022 Waec Biology practical specimen answers or solutions that are on this page are real or genuine? then have it in mind that is 100% accurate, kindly check the specimen question and analyze it with our answer to confirm yourself.
Nkedugists make sure any information from this website is accurate for all students because will understand the pressure of candidates who want success and want to make their parents proud by coming up with good results.
Join our Forum To get our answers for free. let’s get started with the 2022 Waec biology practical specimen answer.
2022 Waec Biology Practical Specimen Listed Below
Specimen A – Weevil-damaged been seed
Specimen B – Viable been seed
Specimen C – Dried Maize grain soaked in water overnight
Specimen D – Soldier termite (dead) done
Specimen E – Honeybee (dead) done
Specimen F – Muddy water ( in a test tube)
Specimen G – Lower jaw of a herbivore with teeth intact done
Specimen H: Head of domestic fowl (complete) done
Specimen J: Quill Feather done
Specimen K: Leg of domestic fowl (complete)
Specimen L: Head of Duck (complete) done
2022 WAEC BIOLOGY PRACTICAL ANSWER IS PROVIDED HERE TO ALL WAEC CANDIDATES
Specimen H: Head of domestic fowl (complete) and Specimen L: Head of Duck (complete)
The phylum of Specimen H and L is Chordata and the class of Specimen H and L is Aves
A(i) Name the habitats of each of specimens H and L.
Specimen H a common environments for include savannas, woodlands, desert, plains, semidesert, dry grasslands and scrubs. . While
Specimen L are found in wetlands, marshes, ponds, rivers, lakes and oceans because they are mostly aquatic birds, and may be found in both fresh water and sea water.
Mode of Feeding of Specimen H and L
They are omnivorous and will eat grass, aquatic plants, insects, seeds, fruit, fish, crustaceans and other types of food.
(ii) Name the class to which of each of specimens H and L belong.
They both belongs Aves
(111) Observable features that adapt specimen L to its habitat
- Ducks possess an oily coating that keeps water from settling in their feathers, helping them in staying dry and keeping themselves warm.
- Their webbed feet, designed like paddles, provide more surface area to push against the water and help them swim.
- The comb-like structure, called pecten, present along the edge of their beak is adapted to hold slippery food and to preen feathers.
- They have specialized flat beak suitable for searching insect larvae and pulling small mollusks, worms, and waterweed out of the mud.
(iv) Behavior Features of Specimen L to its Habitat
- Dabbling ducks take their food on land or the surface of the water, or by reaching as deep as they can without completely submerging. Sea ducks and diving ducks, on the other hand, feed by diving deep underwater.
- To keep themselves clean, ducks often preen themselves by pushing their heads and putting their bills into the body.
- They make different types of calls, including cooing, whistling, grunting, and yodeling. Scaup, for example, makes a call that sounds like ‘scaup’ whereas the mallard makes the typical ‘quack’ sound and another rough noise called the ‘breeeeze’.
- Specimen L migrate during the winter months to somewhere warmer.
Reproduction of Specimen L
Sexual Reproduction and they lay eggs, the eggs usually hatch about 28-35 days after the beginning of incubation.
Drawing Diagram of Specimen L
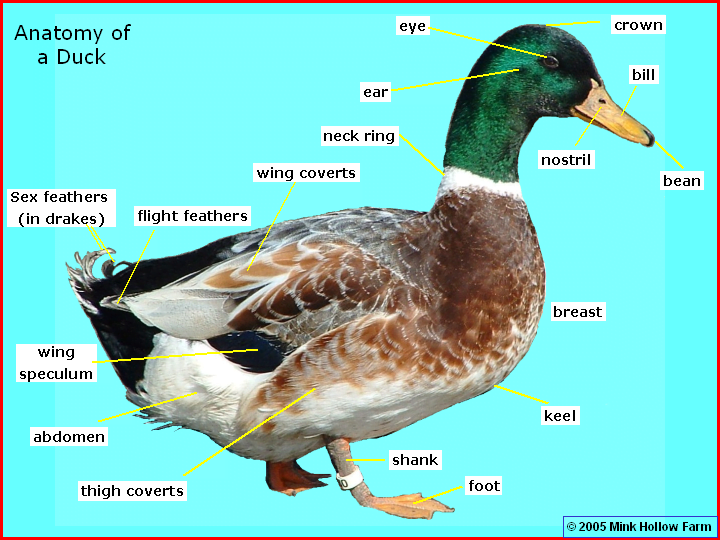
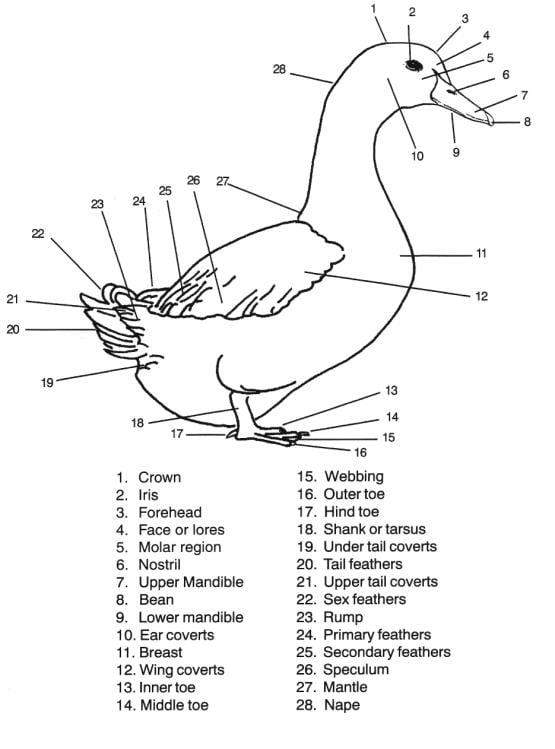
Title (DV)
Quality (Q)
Clarity of lines (CL)
Neatness of labels (NL)
Correct Size (SZ) 8cm-10cm
Magnification (Mg) (x1 – 1½)
Observable features that adapt specimen H to its habitat
The present comb, beak, wattles, ears, earlobes, eyes, eye rings
State:
Three observable similarities between specimens H and L.
Present of beak
Present of eyes and nostril
Present of ear
Three observable differences between specimens H and L.
Specimen H
- Present of crown
- Absent of wattles
- Present of bean
- are found in wetlands, marshes, ponds, rivers, lakes and oceans because they are mostly aquatic birds, and may be found in both fresh water and sea water
Specimen L
- Present of Comb
- Present of wattles
- Absent of bean
- Common environments for include savannas, woodlands, desert, plains, semidesert, dry grasslands and scrubs.
4ci.Identify the sex of specimen H and L
Female
(ii) State one reasons for the answer in 4(c)(i).
Present of comb and crown
(d) Drawing Diagram of Specimen H
Specimen J: Quill Feather
Kingdom and Class of organism from which specimen J/quill feather could be obtained
Kingdom Class
Animalia Aves
(ii) Location on the body of organism from which specimen H/quill feather could be obtained
Wing(s)/tail(s)
(iii) Example of organism from which specimen J/quill feather could be obtained
Pigeon/domestic fowl/cock/hen/dove/vulture/ostrich/gull/duck/any correctly named bird.
(iv) Functions of specimens J to the organisms that possess them
Flight/flying;
Insulation;
Camouflage;
Sexual/courtship display;
Protection;
Waterproof;
Identification;
Gives shape
(vi) observable Features that Adapt Specimen J to Its Habitat
Specimen J
Strong and firm; to beat against air/wind/protection/insulation;
Hollow shaft/rachis/light weight; for buoyancy;
Interlocking barbules/closely packed barbs; for upthrust;
Colour; for camouflage/courtship display/identification;
Glossy surface; for waterproof. other features are below
Barbs present
Vanes present
Vein absent
Shaft/rachis present
Midrib absent
Petiole absent
Smaller in size
Sharp margin absent
Non-green in colour
Barbules present
Calamus present
Inferior/superior umbilicus present
Aftershaft present
Barbs are diagonal
Blunt end
Short barb(s)
Specimen D – Soldier termite (dead)
i) What Kingdom and Class of organisms do specimens D and E
Specimen D – Soldier termite (dead)
Kingdom Class Phylum
Animalia Insecta Arthropoda
ii) Mode of feeding of Specimen D
Specimen D possess strong mandible and maxillae (mouth-parts) which enable them to bite and chew plant parts. Therefore their mode of feeding Biting and Chewing
iii) Economics Important of Specimen D
- Insect pests destroy woods in the home through their biting, and chewing activities
- They are used as food by humans or are fed to livestock
- They are important in nature as decomposers and recyclers of tropical and subtropical dead wood
- They increase the cost of production during the course of controlling them
- They render vegetables and fruits unattractive and unmarketable
- Termites do not carry disease and don’t usually bother buildings because there is not enough water in the wood.
Prevention and Control of Specimen D
- To avoid dampwood termites, make sure water drains away from your house.
- Replace any damp or damaged wood on the outside of your home.
iv) Life Cycle of Specimen D
The life cycle of specimen D is a incomplete metamorphosis stage or life cycle which are from egg, to nymph, and to adult.
Diagram of Specimen /Termite
v) Name of the habitats of Specimen D
Specimen E usually live in damp, dying wood or in houses with leaking plumbing that keeps the wood wet.
vi) Observable Features of Specimen D that Adapt Specimen D to Its Habitat
– Body covered with exoskeleton made of chitin;
– Body up of head, thorax and abdomen/3 – body division;
– Presence of jointed appendages;
– Head bears a pair of jointed antennae;
– Thorax made up of 3 segments/pro-thorax and meta-thorax;
– Thorax bears one or two pairs of wings;
– 3 pairs of jointed legs;
– Abdomen is segmented;
– Presence of spiracles on abdomen.
| Structural differences between Queen Termite & Soldier Termite | |
| A/Queen | B/Soldier |
| – Distended/large abdomen; | – Small abdomen; |
| – Small head; | – Large head; |
| – Mandible absent; | – Presence of powerful mandibles; |
| – Conspicuous spiracles; | – No spiracles seen/invisible spiracle/spiracles absent (in diagram) |
| – Patches of hardened cuticle present; | – Patches of hardened cuticle absent; |
| Eye present. | – Eye absent |
Observable adaptive features of
Queen Termite
– Presence of eye; to see
– Large/distended abdomen; to carry many eggs
Soldier Termite
- Presence of antenna; to detect intruder/changes in the termitarium;
- Large/powerful mandibles; for defence/offence.
Specimen E – Honeybee (dead)
i) What Kingdom and Class of organisms do specimens E
Kingdom Class Phylum
Animalia Insecta Arthropoda
ii) Mode of feeding of Specimen E
The mouthparts of Specimen E are chewing and lapping type.
iii) Life Cycle of Specimen E
The life cycle of specimen E is a complete metamorphosis stage or life cycle – Which is from egg to Larvae to pupa to Adult
iv) Name of the habitats of Specimen E
prefer to live in gardens, woodlands, orchards, meadows and other areas where flowering plants are abundant.
vi) Economics importance of Specimen E
- Some are carriers or vectors of diseases
- The profits of farmers are reduced
- They reduce the quality of produce either in the store or in the field
- They generally reduce the yield of crops
- They can also cause total death of crop plants
Diagram of Specimen E/Honeybee
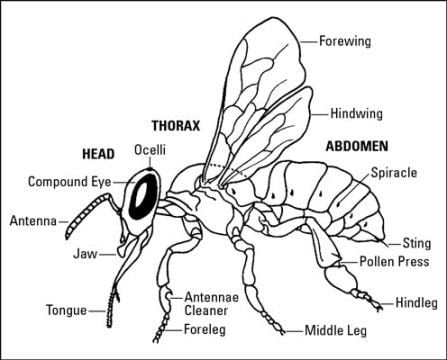
iv) Observable Features of Specimen E
- They have a hard outer shell called an exoskeleton.
- They have three main body parts: head, thorax, abdomen.
- They have a pair of antennae that are attached to their head.
- They have three pairs of legs used for walking.
- They have two pairs of wings.
Observable Features of Specimen E that Adapt Specimen E to Its Habitat
Head Location of the eyes, brain, where the antennae attach.
Present of weak Mandibles outer mouthparts that help protect the proboscis.
Present of weak Proboscis Tube-like mouth part used to suck up fluids.
Closed Ocelli One of two types of insect eyes used to detect motion.
Dead Eye (Compound) which is made of many light detectors called ommatidia.
Present of dead Antenna segmented feelers that detect airborne scents and currents.
Thorax Midsection where the (6) legs and wings attach.
Absent of Forewings Wings closest to the head ( dead honeybee).
Hind Wings Wings farthest from the head.
Forelegs Legs closest to the head.
Prevention and Control Specimen E
- By Physical control
- By Cultural control
- By Biological control
(ii) State three similarities between specimens D and E
- Both have the present of outer shell called an exoskeleton.
- They have three main body parts: head, thorax, abdomen.
- They have a pair of antennae that are attached to their head.
- They have three pairs of legs used for walking.
- They have two pairs of wings.
(iii) State two differences between specimens D and E (3 marks )
Specimen D
- Their mode of feeding Biting and Chewing
- The life cycle of specimen D is incomplete metamorphosis stage
Specimen E
- Their mode chewing and lapping type.
- The life cycle of specimen E is a complete metamorphosis stage
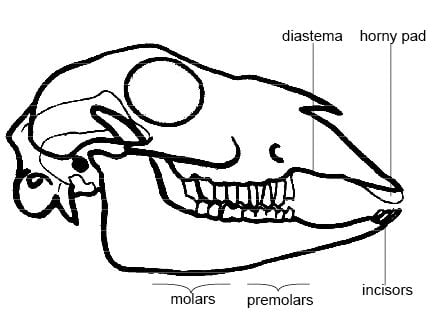
Specimen G – Lower jaw of a herbivore with teeth intact
What teeth does Specimen G have?
The dental formula of herbivores, like cattle that feed on fodder, is 2 x ( 033 / 433 ) = 32
Diagram of Specimen G
They can bring back food to the mouth that they have swallowed previously for chewing it again. This helps them in absorbing the nutrients completely from any kind of food that is hard to chew. Examples include cows and camels.
They do not need to chew on their food at all. Their mouths are shaped in the form of a straw to help them suck nectar from flowers. Examples include moths and butterflies.
Sharp incisor-like front teeth are present in certain herbivores for them to gnaw and break down certain food items.
- They can move their jaws in a sidewards motion, which helps them to eat.
Observable Features of Specimen G that Adapt Specimen G to Its Habitat
Special Teeth
Alkaline Saliva
Herbivores have alkaline saliva, which means their digestion process is slower as compared to carnivores who have acidic saliva and start digesting food as soon as it is ingested. Also, the plants’ herbivores feed on, go through a preparatory process that makes them easy to digest.


34 Comments
please do you have fishery obj and theory questions and answer for 2022. I really need it .
Very good
Thanks
Hi
Thanks 👍
Pls do u have chemistry practical and essay questions Nd answer
Whatsapp or call mr James today for your jamb upgrade for those who didn’t perform well on their exams 08055826042
Okays
Very good
Please I need the agriculture pratical answer B4 Monday
2022
Please do u have account question and theory
Thanks so much for this you guys really helped in agric practicals
Oh wow this is wonderful am so happy for you, does he have a group? I want to join tho
God bless you ☺️
Thanks u oo
But pls is this really the real question !
Pls I want to be sure
Yes
Me too am confused
Oh wow
Thanks for d answer. This is the exact waec specimen dey gave me cos am a biology teacher
Thank u very much good of you
I need biology answers
Nice one
Thanks and God bless you 🙏
Please do you have further mathematics 2022 questions, really need it
I love you keep it up
Nice the specimen are correct dude.
Thank you very much for this I really appreciate it
Pls I need agriculture theory question and answer
Thanks guys
Thanks very useful indeed
Further mathematics questions and answers pls
Thank you very much,this is really helpful. Please I need agricultural science solutions before Tuesday.
Thanks so much. It’s actually the correct one
Thank you very much am much great full
Please are the biology practical question from 2022